Weight Watchers Starting Points Calculator
The purpose behind Weight Watchers™ daily smart point allowance can be summarized within one simple principal, to maintain a daily caloric intake lower than that which would otherwise maintain your current bombshell physique.
It's that simple. The daily points you are allocated force you to eat less than what your body needs to stay at its current weight.
Thus, your daily point allowance is designed to assist you in losing between 1 to 2 pounds per week. Although two pounds a week might not sound like a lot at first, it is the CDC recommended rate for healthy, sustainable weight loss and as we step through some of the equations used to derive the Weight Watcher point system, it will become more evident that a little is actually a lot when it comes to losing weight!
To answer this, we need to start by breaking down the main components Weight Watchers uses to determine the daily points allowance that would sustain your current weight. From there we can infer the SmartPoint allowance necessary for healthy, sustainable weight loss. These are the three main processes of metabolism WW uses to calculate your daily points:
1. Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
- Consumes between 60-70% of the energy we burn each day
- For example, keeping our heart beating & mechanical processes such as breathing
2. Physical Activity Level (PAL)
- Consumes between 20-30% of the energy we burn each day
- Increases as the intensity of activity increases
3. Food Digestion
- Accounts for about 10% of our daily energy consumption.
- Also referred to as the thermic effect of food (TEF)
By assigning numerical values to these metabolic components, we can esimate our Total Daily Energy Expediture (TDEE), which will represent the calories we would need each day to sustain our current body weight. From there, losing weight is as simple as following a system like Weight Watchers to ensure we consume between 500 and 1000 less calories per day in order to meet our objective of losing 1 to 2 pounds per week!
This is the equation we are going to solve for in the follow example:
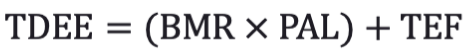
Where BMR stands for Basal Metabolic Rate, PAL stands for Physical Activity Level, and TEF stands for the Thermic Effect of Food. Once we know our TDEE value, we can use it as a baseline for our projected daily points allowance.
These are the steps how to do it...
1. Calculate BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate)
Unless you know your exact body fat percentage, Mifflin-St and Jeor's (1990) revision of the original Harris-Benedict equation (1918), is our best predictive indicator of BMR to date. It requires your height, weight, age, and gender in order to estimate BMR within ±200 calories.
BMR For Men:
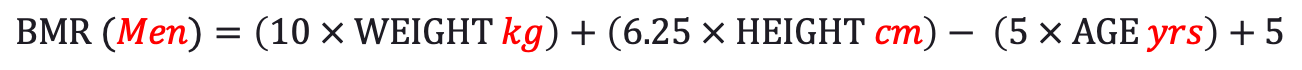
BMR For Women:
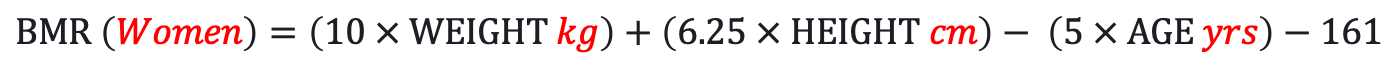
If you're wondering how these seemingly random values were determined, they were proven through regression analysis of experimental data. Ok, now that we know the equations, let's calculate the BMR for a 35 year old male with the following attributes:
| Gender | Male |
| Age | 35 years |
| Height | 5' 10'' (178 cm) |
| Weight | 200 lbs (91 kg) |
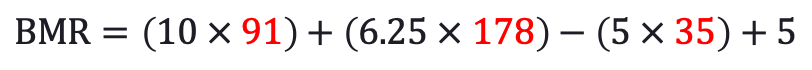
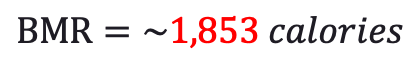
Therefore, a five-foot-ten, two hundred pounds, thirty-five year old male will burn about 1,853 calories simply by getting out of bed in the morning and navigating a typical daily routine.
2. Factor in Physical Activity Level (PAL)
Now that we have calculated BMR, it's time to factor in physical activity level (PAL). The following table describes activity levels and their associated PAL multiplier:
| Activity Level | Description | PAL |
| Inactive/Sedentary | Desk job with no option to move around; little to no strenuous leisure activity | 1.25 |
| Light Activity | Desk job that requires you to move around; little to no strenuous leisure activity | 1.5 |
| Moderate Exercise | Standing work; Some strenuous leisure activity | 1.75 |
| Heavy Exercise | Strenuous work or highly strenuous leisure activity | 2.0 |
Multipliers may slightly differ depending on source
We can now use one of these PAL to solve for the segment of the TDEE equation. Let's continue our example by factoring in a physical activity level of Inactive/Sedentary (since most of us will fit into this category anyway) using the BMR from our previous calculation.
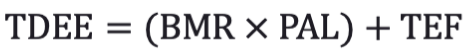


Great, let's move on to the final step in calculating Total Energy Expenditure!
3. Account for the Thermic Effect of Food (TEF)
Now that we have accounted for Basal Metabolic Rate and Physical Activity Level, the final metabolic component that affects TDEE is food digestion, which is scientifically referred to as the Thermic Effect of Food or TEF for short.
If you recall from earlier, food digestion can be measured to consume an additional 10% of daily energy consumption, therefore, our TEF equation will do just that:
We've successfully solved for all the elements necessary to calculate TDEE in our example, so let's do that!
And... we're done! This means that our 5ft 10in, 200lb, 35 year-old, sedentary male will consume about 2,501 calories a day just by existing and not making any additional effort to burn calories or consume energy. What this number also indicates, are the number of calories this individual needs to consume to remain his current weight.
Once we're armed with this number, losing weight is as simple as dropping our daily caloric intake below this value at a rate of 500 calories per pound! The following chart demonstrates how our daily intake would need to be adjusted to lose 1, 1.5, and 3 pounds a week:
| Pounds Per Week | Calories Per Day |
|---|---|
| 1 pound | 2,001 calories |
| 1.5 pounds | 1,751 calories |
| 2 pounds | 1,501 calories |
calories are short-hand for kilocalories (kcal)
To lose between 1 and 2 pounds a week, the individual in our example would need to consume between 1,501 and 2,001 calories a day. Now that we have these numerical metrics to reference, it's easy to see why the CDC recommends this range as an optimal weight loss rate, 1,000 fewer calories a day is a lot!
That's great and all, but...
In order to answer this, we must first calculate the daily smart point allowance for our example using the Weight Watchers formula:
| If you are a male | 8 points |
| Between ages 27-37 | 3 points |
| One point per 10 lbs | 20 points |
| 5 ft 10 in + | 2 points |
| Sedentary/Inactive | 0 points |
| Total | 33 points |
The Weight Watchers method allows our example participant 33 daily smart points, in addition to 49 weekly points. If we factor in our weekly smart points as an average per day, we would get:
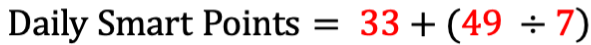
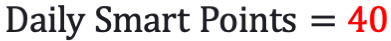
So, on average, we have 40 smart points to spend per day. Although, this value is accurate for our first week, it should be recalculated each week to account for any weight loss that could affect the allowance value.
Now that we have solved for TDEE (the number of calories to sustain our current weight) and our daily smart point allowance, I'd imagine the most common mistake at this point would be to correlate smart points directly to calories. This is because not all calories are created equal and their relative worth will differ depending on their origin. One way to visualize how Weight Watchers stresses this point is to take saturated fat, sugar, and protein and represent them through calories per smart point.
| Nutrient Type | Calories Per Smart Point |
|---|---|
| Saturated Fat | 17 |
| Sugar | 24 |
| Protein | 48 |
| Average | ~ 30 |
Thus, if you come across a thread or post that indicates a smart point is equivalent to 30 calories, this is why. However, as we'll find out, this is a bit of a misconception. Because, if we take this arithmetic mean and apply it to our adjusted daily allowance points, we get:
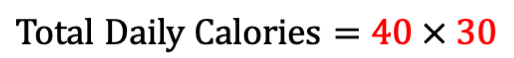
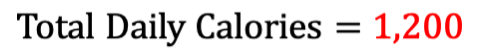
Considerably lower than what we should expect, which would be somewhere between 1,500 and 2,000 calories to achieve our weight loss goals healthily and sustainably. Thus, taking the arithmetic mean of calories per smart point, in essence, the assumption that all calories are created equal is not the recipe Weight Watchers subscribes to.
But what if we take our calorie per smart point metrics and weight them to align with CDC recommended guidelines for saturated fat and sugar consumption? Both of which should account for 10% of your daily caloric intake. So, let's allocate these percentages to our daily smart points and analyze the results:
| Nutrient Type | Weighted Point Value | Points × Calories Per SmartPoint | Calories |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saturated Fat | 4 points (10% of 40 points) | 4 × 17 | 68 |
| Sugar | 4 points (10% of 40 points) | 4 × 24 | 96 |
| Protein | 32 points (80% of 40 points) | 32 × 48 | 1536 |
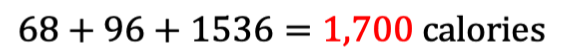
Which equals about 800 fewer calories a day from our original TDEE value of 2,501 calories and if we translate that into an expected weight loss rate, it would be 1.6 pounds per week - exactly where we need to be!
Weight Watchers Starting Points Calculator
Source: https://www.watcherspoint.com/allowance-calculator


0 Komentar